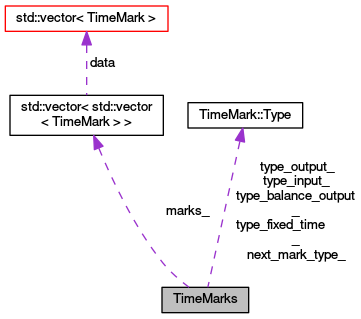
This class is a collection of time marks to manage various events occurring during simulation time. More...
#include <time_marks.hh>
Public Types | |
| typedef TimeMarksIterator | iterator |
| Iterator class for iteration over time marks of particular type. This is always const_iterator. More... | |
Private Attributes | |
| TimeMark::Type | next_mark_type_ |
| MarkType that will be used at next new_time_mark() call. More... | |
| std::vector< std::vector< TimeMark > > | marks_ |
| TimeMarks list sorted according to the their time. More... | |
| TimeMark::Type | type_fixed_time_ |
| Predefined type for fixed time. More... | |
| TimeMark::Type | type_output_ |
| Predefined type for output. More... | |
| TimeMark::Type | type_input_ |
| Predefined type for change of boundary condition. More... | |
| TimeMark::Type | type_balance_output_ |
| Predefined type for balance output. More... | |
Friends | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &stream, const TimeMarks &marks) |
| Friend output operator. More... | |
Detailed Description
This class is a collection of time marks to manage various events occurring during simulation time.
TimeMark and their types
One TimeMark consists of time and type (TimeMark::Type), see the constructor TimeMark::TimeMark. The type of mark is bitmap where individual bits corresponds to some base event types like changing a BC, output solution, coupling time with another equation and so on. Base types can be combined by bitwise or (operator|).
Special types are predefined in TimeMarks class. These are returned by their getters:
- type_fixed_time() - marks of this type are considered as fixed times by a TimeGovernor which is connected to particular TimeMarks object.
- type_output() - this type marks times at which solution should be computed and written to output.
- type_bc_change() - this type marks times at which BC is is changed and model has to be updated.
TimeMarks collection
TimeMarks collect marks of various types and provides methods for iterating over stored marks. You can selectively access only marks matching given type mask. See TimeMark::match_mask.
You can add one new mark through method add or add evenly spaced marks of same type by TimeMarks::add_time_marks.
You can allocate new TimeMark::Type in the context of one TimeMarks object by TimeMarks::new_mark_type.
For a given TimeGovernor (not necessarily connected one) you can ask about existence of mark in current time interval (TimeMarks::is_current) and see TimeMarks close to the current time (TimeMarks::next and TimeMarks::last). The current time interval is left-open and right-closed: (t,t+dt]. Repeatedly used TimeMarks::next always returns the same TimeMark if the time of the TimeGovernor is not changed.
In most cases there will be only one TimeMarks object for the whole solved problem and used by TimeGovernors of individual equations. However this is not necessary.
- See also
- TimeMark
Definition at line 197 of file time_marks.hh.
Member Typedef Documentation
| typedef TimeMarksIterator TimeMarks::iterator |
Iterator class for iteration over time marks of particular type. This is always const_iterator.
Definition at line 201 of file time_marks.hh.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| TimeMarks::TimeMarks | ( | ) |
Default constructor.
Definition at line 45 of file time_marks.cc.
Member Function Documentation
Basic method for inserting TimeMarks.
- Parameters
-
mark Reference to TimeMark object.
Definition at line 82 of file time_marks.cc.
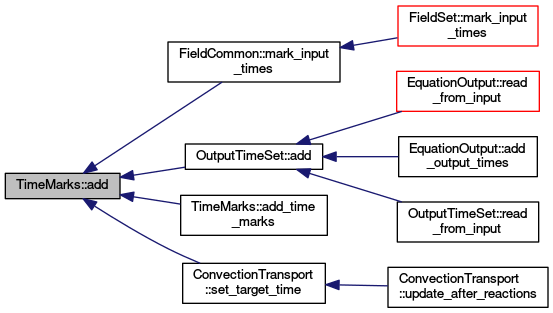
| void TimeMarks::add_time_marks | ( | double | time, |
| double | dt, | ||
| double | end_time, | ||
| TimeMark::Type | type | ||
| ) |
Method for creating and inserting equally spaced TimeMarks.
- Parameters
-
time Time of the first TimeMark. dt Lenght of interval between equally spaced TimeMarks. end_time No marks after the end_time. type Type of inserted TimeMarks or their combinations.
Current lazy implementation have complexity O(m*n) where m is number of inserted time marks and n number of time marks in the array. TODO: O(n+m) implementation
Definition at line 107 of file time_marks.cc.
| void TimeMarks::add_to_type_all | ( | TimeMark::Type | filter_type, |
| TimeMark::Type | add_type | ||
| ) |
Apply TimeMark::add_to_type (|=) to all time marks matching the filter type.
Definition at line 119 of file time_marks.cc.
| TimeMarks::iterator TimeMarks::begin | ( | TimeMark::Type | mask | ) | const |
Iterator for the begin mimics container-like of TimeMarks.
Definition at line 193 of file time_marks.cc.
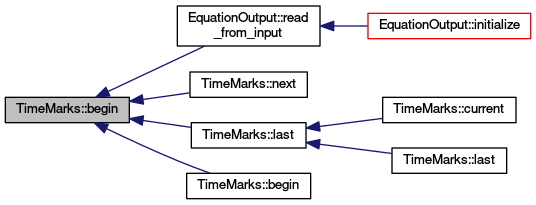
| TimeMarks::iterator TimeMarks::begin | ( | unsigned char | ei | ) | const |
Same as previous, but constructs TimeMark::Type from equation index.
Definition at line 200 of file time_marks.cc.
| TimeMarks::iterator TimeMarks::current | ( | const TimeStep & | time_step, |
| const TimeMark::Type & | mask | ||
| ) | const |
Definition at line 142 of file time_marks.cc.
| TimeMarks::iterator TimeMarks::end | ( | TimeMark::Type | mask | ) | const |
Iterator for the end mimics container-like of TimeMarks.
Definition at line 207 of file time_marks.cc.
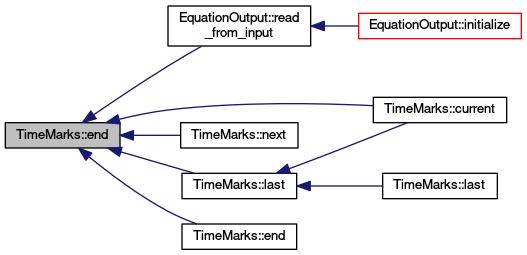
| TimeMarks::iterator TimeMarks::end | ( | unsigned char | ei | ) | const |
Same as previous, but constructs TimeMark::Type from equation index.
Definition at line 214 of file time_marks.cc.
| TimeMarks::iterator TimeMarks::last | ( | const TimeStep & | time_step, |
| const TimeMark::Type & | mask | ||
| ) | const |
Return the last TimeMark with time less or equal to tg.time() that match the mask. The time governor tg is used also for time comparisons.
- Parameters
-
tg the time governor mask mask of marks to iterate on
Definition at line 166 of file time_marks.cc.
| TimeMarks::iterator TimeMarks::last | ( | const TimeGovernor & | tg, |
| const TimeMark::Type & | mask | ||
| ) | const |
Definition at line 178 of file time_marks.cc.
| TimeMarks::iterator TimeMarks::last | ( | const TimeMark::Type & | mask | ) | const |
Returns iterator to the last time mark matching given mask.
Definition at line 184 of file time_marks.cc.
| TimeMark::Type TimeMarks::new_mark_type | ( | ) |
Add a new base mark within the context of the particular TimeMarks instance. User should keep the returned value (MarkType is basically a bitmap) for further queries and TimeMark insertions. ATTENTION: You can not use the TimeMark::Type with other TimeMarks instance! Types are added as they are prepared in next_mark_type_. Next mark type is updated by (left) bit shifting operator.
Definition at line 69 of file time_marks.cc.
| TimeMarks::iterator TimeMarks::next | ( | const TimeGovernor & | tg, |
| const TimeMark::Type & | mask | ||
| ) | const |
Return the first TimeMark with time strictly greater then tg.time() that match the mask. The time governor tg is used also for time comparisons.
- Parameters
-
tg the time governor mask mask of marks to iterate on
TODO: have also method which accepts double (time) instead of the whole TimeGovernor. and compare without safety.
Definition at line 150 of file time_marks.cc.
| void TimeMarks::reinit | ( | ) |
Reset state after construction (through default constructor). Useful for unit tests.
Definition at line 52 of file time_marks.cc.

|
inline |
Predefined base TimeMark type for times of balnace output. Is defined by constructor as 0x08.
Definition at line 240 of file time_marks.hh.
|
inline |
Predefined base TimeMark type that is taken into account by the TimeGovernor. Is defined by constructor as 0x01.
Definition at line 225 of file time_marks.hh.
|
inline |
Predefined base TimeMark type for times when the boundary condition is changed. Is defined by constructor as 0x04.
Definition at line 235 of file time_marks.hh.
|
inline |
Predefined base TimeMark type for output times. Is defined by constructor as 0x02.
Definition at line 230 of file time_marks.hh.
Friends And Related Function Documentation
|
friend |
Friend output operator.
Member Data Documentation
|
private |
TimeMarks list sorted according to the their time.
Definition at line 322 of file time_marks.hh.
|
private |
MarkType that will be used at next new_time_mark() call.
Definition at line 319 of file time_marks.hh.
|
private |
Predefined type for balance output.
Definition at line 331 of file time_marks.hh.
|
private |
Predefined type for fixed time.
Definition at line 325 of file time_marks.hh.
|
private |
Predefined type for change of boundary condition.
Definition at line 329 of file time_marks.hh.
|
private |
Predefined type for output.
Definition at line 327 of file time_marks.hh.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- /opt/flow123d/flow123d/src/tools/time_marks.hh
- /opt/flow123d/flow123d/src/tools/time_marks.cc
 1.8.11
1.8.11