Basic time management functionality for unsteady (and steady) solvers (class Equation). More...
#include <time_governor.hh>
Public Member Functions | |
| DECLARE_INPUT_EXCEPTION (ExcTimeGovernorMessage,<< EI_Message::val) | |
| TimeGovernor (const Input::Record &input, TimeMark::Type fixed_time_mask=TimeMark::none_type) | |
| Constructor for unsteady solvers. More... | |
| TimeGovernor (double init_time=0.0, TimeMark::Type fixed_time_mask=TimeMark::none_type) | |
| Default constructor - steady time governor. More... | |
| TimeGovernor (double init_time, double dt) | |
| void | set_permanent_constraint (double min_dt, double max_dt) |
| Sets permanent constraints for time step. More... | |
| int | set_upper_constraint (double upper) |
| Sets upper constraint for the next time step estimating. More... | |
| int | set_lower_constraint (double lower) |
| Sets lower constraint for the next time step estimating. More... | |
| double | fix_dt_until_mark () |
| Fixing time step until fixed time mark. More... | |
| void | next_time () |
| Proceed to the next time according to current estimated time step. More... | |
| TimeMark::Type | equation_mark_type () const |
| TimeMark::Type | equation_fixed_mark_type () const |
| void | add_time_marks_grid (double step, TimeMark::Type mark_type=TimeMark::none_type) const |
| bool | is_current (const TimeMark::Type &mask) const |
| TimeMarks::iterator | next (const TimeMark::Type &mask) const |
| TimeMarks::iterator | last (const TimeMark::Type &mask) const |
| double | upper_constraint () const |
| double | lower_constraint () const |
| double | end_of_fixed_dt () const |
| bool | is_changed_dt () const |
| double | t () const |
| double | last_dt () const |
| double | last_t () const |
| double | dt () const |
| double | estimate_dt () const |
| Estimate choice of next time step according to actual setting of constraints. More... | |
| double | estimate_time () const |
| double | end_time () const |
| End time. More... | |
| bool | is_end () const |
| Returns true if the actual time is greater than or equal to the end time. More... | |
| bool | is_steady () const |
| Returns true if the time governor is used for steady problem. More... | |
| bool | gt (double other_time) const |
| bool | ge (double other_time) const |
| bool | lt (double other_time) const |
| bool | le (double other_time) const |
| int | tlevel () const |
| void | view (const char *name="") const |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static TimeMarks & | marks () |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static Input::Type::Record | input_type |
| static const double | inf_time = numeric_limits<double>::infinity() |
| Infinity time used for steady case. More... | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | init_common (double dt, double init_time, double end_time, TimeMark::Type type) |
| Common part of the constructors. Set most important parameters, check they are valid and set default values to other. More... | |
Private Attributes | |
| int | time_level_ |
| Number of time_next calls, i.e. total number of performed time steps. More... | |
| double | init_time_ |
| Initial time. More... | |
| double | time_ |
| End of actual time interval; i.e. where the solution is computed. More... | |
| double | last_time_ |
| Beginning of the actual time interval; i.e. the time of last computed solution. More... | |
| double | end_of_fixed_dt_interval_ |
| End of interval if fixed time step. More... | |
| double | end_time_ |
| End time of the simulation. More... | |
| double | time_step_ |
| Length of actual time interval; i.e. the actual time step. More... | |
| double | last_time_step_ |
| Time step just before last_time. More... | |
| double | fixed_time_step_ |
| Next fixed time step. More... | |
| bool | is_time_step_fixed_ |
| Flag that is set when the fixed step is set (lasts only one time step). More... | |
| bool | time_step_changed_ |
| Flag is set if the time step has been changed (lasts only one time step). More... | |
| double | upper_constraint_ |
| Upper constraint for the choice of the next time step. More... | |
| double | lower_constraint_ |
| Lower constraint for the choice of the next time step. More... | |
| double | max_time_step_ |
| Permanent upper limit for the time step. More... | |
| double | min_time_step_ |
| Permanent lower limit for the time step. More... | |
| TimeMark::Type | eq_mark_type_ |
| TimeMark type of the equation. More... | |
| bool | steady_ |
| True if the time governor is used for steady problem. More... | |
Static Private Attributes | |
| static const double | time_step_lower_bound = numeric_limits<double>::epsilon() |
| Technical bound for the time step given by finite precision. More... | |
| static const double | round_n_steps_precision = 1e-14 |
| Rounding precision for computing number of steps. Used in estimate_dt(). More... | |
| static TimeMarks | time_marks_ = TimeMarks() |
Detailed Description
Basic time management functionality for unsteady (and steady) solvers (class Equation).
Common features and unsteady time governor (TG)
This class provides algorithm for selecting next time step, and information about current time step frame. Step estimating is constrained by several bounds (permanent maximal and minimal time step, upper and lower constraint of time step). The permanent constraints are set in the constructor from the input record so that user can set the time step constraints for the whole model. Function set_permanent_constraint() should be used only in very specific cases and possibly right after the constructor before using other functions of TG.
Choice of the very next time step can be constrained using functions set_upper_constraint() and set_lower_constraint(). Lower and upper constraints are set equal to permanent ones in the constructor and can only become stricter. If one tries to set these constraints outside the interval of the previous constraints, nothing is changed and a specified value is returned. Upper and lower constraints are reset in function next_time() to the permanent constraints.
The later one can be called multiple times with various constraint values and we use the minimum of them. Function next_time() choose the next time step in such a way that it meets actual constraints and a uniform discrete time grid with this step hits the nearest fixed time in lowest possible number of steps.
The fixed times are time marks of TimeMarks object passed at construction time with particular mask.
There is just one set of time marks for the whole problem. Therefore TimeMarks object is static and is shared umong all the equations and time governors. Each equation creates its own specific time mark type.
Solution of the next time step proceeds in following steps:
- Estimate next time step and set constraints (this can be usefull in hc_seq_explicit for estimating next transport time)
- Fix next time step up to the next time mark (this is necessary for ConvectionTransport)
- Proceed to the next time when solution is available. (this can replace solved flag in equation classes)
Information provided by TG includes:
- actual time, last time, end time
- actual time step
- number of the time level
- end of interval with fixed time step
- time comparison
- static pointer to time marks
Steady time governor
Steady TG can be constructed by default constructor (initial time is zero) or by constructor with initial time as parameter. End time and time step are set to infinity. One can check if the time governor is steady by calling is_steady(). Calling estimate_dt() will return infinity.
Setting constraints have no consequences. Calling fix_dt_until_mark() will only return zero and will not do anything.
The steady TG works in two states. At first the time is set to initial and time level is equal zero. To use steady TG properly one should call next_time() after the computation of steady problem is done. Current time is then set to infinity, time level is set to 1 and calling estimate_dt() will return zero.
Note: For example class TransportNothing (which computes really nothing) uses also steady TG but it calls next_time() immediately after TG's construction. This means that the 'computation'of transport is done.
TODO:
- still we have problems with time comparisons 1) TimeMarks can merge marks only with fixed precision, since they are shared by several equations with possibly different timesteps. 2) On the other hand comparing of times by time governor can be done relatively to the current time step.
Definition at line 119 of file time_governor.hh.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| TimeGovernor::TimeGovernor | ( | const Input::Record & | input, |
| TimeMark::Type | fixed_time_mask = TimeMark::none_type |
||
| ) |
Constructor for unsteady solvers.
- Parameters
-
input accessor to input data fixed_time_mask TimeMark mask used to select fixed time marks from all the time marks. This value is bitwise added to the default one defined in TimeMarks::type_fixed_time().
Definition at line 71 of file time_governor.cc.
|
explicit |
Default constructor - steady time governor.
We can have "zero step" steady problem (no computation, e.g. EquationNothing) and one step steady problem (e.g. steady water flow).
Time is set to zero, time step and end time to infinity.
First call of next_time() pushes the actual time to infinity.
However, you have to use full constructor for the "steady problem" that has time-variable input data.
Has a private pointer to static TimeMarks and can access them by marks().
Definition at line 101 of file time_governor.cc.
| TimeGovernor::TimeGovernor | ( | double | init_time, |
| double | dt | ||
| ) |
The aim of this constuctor is simple way to make a time governor without Input interface.
TODO: Partially tested as part of field test. Needs its own unit test.
Definition at line 94 of file time_governor.cc.
Member Function Documentation
| void TimeGovernor::add_time_marks_grid | ( | double | step, |
| TimeMark::Type | mark_type = TimeMark::none_type |
||
| ) | const |
Add sequence of time marks starting from the initial time up to the end time with given step. Time marks type combines given mark_type (none by default) and native mark type of the time governor.
Definition at line 248 of file time_governor.cc.

| TimeGovernor::DECLARE_INPUT_EXCEPTION | ( | ExcTimeGovernorMessage | , |
| << EI_Message::val | |||
| ) |
|
inline |
Length of actual time interval; i.e. the actual time step.
Definition at line 308 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
End of interval with currently fixed time step. Can be changed by next call of method fix_dt_until_mark.
Definition at line 276 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
End time.
Definition at line 332 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Specific time mark of the fixed times of the equation owning the time governor.
Definition at line 234 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Specific time mark of the equation owning the time governor.
Definition at line 228 of file time_governor.hh.
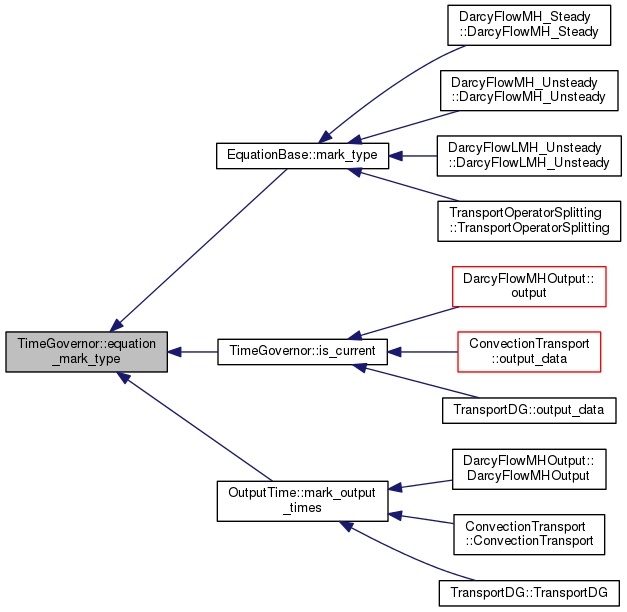
| double TimeGovernor::estimate_dt | ( | ) | const |
Estimate choice of next time step according to actual setting of constraints.
Precedence of constraints:
- meet next fixed time (always satisfied)
- permanent upper constraint (always satisfied)
- upper constraint (always satisfied)
- lower constraint (satisfied if not in conflict with 1.)
- permanent lower constraint (satisfied if 4.)
- else writes the difference between lower constraint and estimated time step
Definition at line 264 of file time_governor.cc.
|
inline |
Estimate next time.
Definition at line 328 of file time_governor.hh.

|
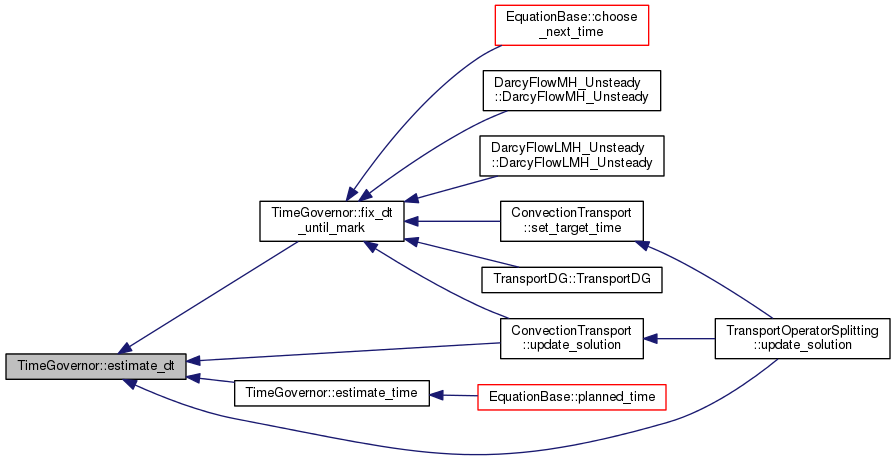
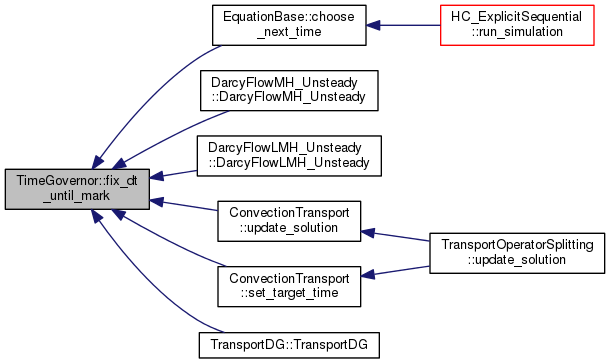
inline |
Fixing time step until fixed time mark.
Fix time step until first fixed time mark. When called inside an already fixed interval, it overwrites previous setting.
- Returns
- actual end of fixed time step.
Definition at line 211 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
|
inline |
Performs rounding safe comparison time > other_time, i.e. time is strictly greater than given parameter other_time with precision relative to the magnitude of the numbers time step. TODO: introduce type TimeDouble with overloaded comparison operators, use it consistently in TimeMarks.
Performs rounding safe comparison time >= other_time See
Performs rounding safe comparison time < other_time. See
Performs rounding safe comparison time <= other_time. See
Definition at line 348 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Common part of the constructors. Set most important parameters, check they are valid and set default values to other.
Set main parameters to given values. Check they are correct. Distinguish fixed time step and variable time step case. Set soft and permanent constrains to the same, the least restricting values. Set time marks for the start time and end time (if finite).
Definition at line 113 of file time_governor.cc.
|
inline |
Getter for dt_changed. Returns whether the time step has been changed.
Definition at line 282 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Simpler interface to TimeMarks::is_current().
Definition at line 246 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Returns true if the actual time is greater than or equal to the end time.
Definition at line 336 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Returns true if the time governor is used for steady problem.
Definition at line 340 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Simpler interface to TimeMarks::last().
Definition at line 258 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Previous time step.
Definition at line 295 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Previous time.
Definition at line 301 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Definition at line 376 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Returns lower constraint.
Definition at line 270 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
|
inlinestatic |
Getter for time marks.
Definition at line 130 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Simpler interface to TimeMarks::next().
Definition at line 252 of file time_governor.hh.
| void TimeGovernor::next_time | ( | ) |
Proceed to the next time according to current estimated time step.
Definition at line 301 of file time_governor.cc.
| int TimeGovernor::set_lower_constraint | ( | double | lower | ) |
Sets lower constraint for the next time step estimating.
- Returns
- -1, 0 or 1 according to the success.
- See also
- set_upper_constrain().
Definition at line 222 of file time_governor.cc.
| void TimeGovernor::set_permanent_constraint | ( | double | min_dt, |
| double | max_dt | ||
| ) |
Sets permanent constraints for time step.
This function should not be normally used. These values are to be set in constructor from the input record or by default.
- Parameters
-
min_dt is the minimal value allowed for time step max_dt is the maximal value allowed for time step
Definition at line 178 of file time_governor.cc.
| int TimeGovernor::set_upper_constraint | ( | double | upper | ) |
Sets upper constraint for the next time step estimating.
This function can only make the constraint stricter. Upper constraint is reset to max_dt in next_time().
- Parameters
-
upper is the upper constraint for time step
- Returns
- -1, 0 or 1 according to the success
- -1: constraint is higher than the permanent upper constraint
max_dt. Setting failed, no change happened. - 0: constraint is in the interval of permanent constraints
min_dtandmax_dt. The upper constraint has been set. - 1: constraint is lower than permanent lower constraint
min_dt. Setting failed, no change happened.
Definition at line 198 of file time_governor.cc.
|
inline |
End of actual time interval; i.e. where the solution is computed.
Definition at line 289 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Returns the time level.
Definition at line 385 of file time_governor.hh.
|
inline |
Getter for upper constrain.
Definition at line 264 of file time_governor.hh.

| void TimeGovernor::view | ( | const char * | name = "" | ) | const |
Prints output of TimeGovernor.
- Parameters
-
name is the name of time governor that you want to show up in output (just for your convenience)
Definition at line 347 of file time_governor.cc.
Member Data Documentation
|
private |
End of interval if fixed time step.
Definition at line 427 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
End time of the simulation.
Definition at line 429 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
TimeMark type of the equation.
Definition at line 461 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Next fixed time step.
Definition at line 436 of file time_governor.hh.
|
static |
Infinity time used for steady case.
Definition at line 396 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Initial time.
Definition at line 421 of file time_governor.hh.
|
static |
Definition at line 125 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Flag that is set when the fixed step is set (lasts only one time step).
Definition at line 438 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Beginning of the actual time interval; i.e. the time of last computed solution.
Definition at line 425 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Time step just before last_time.
Definition at line 434 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Lower constraint for the choice of the next time step.
Definition at line 446 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Permanent upper limit for the time step.
Definition at line 448 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Permanent lower limit for the time step.
Definition at line 450 of file time_governor.hh.
|
staticprivate |
Rounding precision for computing number of steps. Used in estimate_dt().
Definition at line 415 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
True if the time governor is used for steady problem.
Definition at line 464 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
End of actual time interval; i.e. where the solution is computed.
Definition at line 423 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Number of time_next calls, i.e. total number of performed time steps.
Definition at line 418 of file time_governor.hh.
When the next time is chosen we need only the lowest fix time. Therefore we use minimum priority queue of doubles based on the vector container. This is one global set of time marks for the whole problem and is shared among all equations. Therefore this object is static constant pointer.
Definition at line 458 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Length of actual time interval; i.e. the actual time step.
Definition at line 432 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Flag is set if the time step has been changed (lasts only one time step).
Definition at line 440 of file time_governor.hh.
|
staticprivate |
Technical bound for the time step given by finite precision.
Definition at line 413 of file time_governor.hh.
|
private |
Upper constraint for the choice of the next time step.
Definition at line 444 of file time_governor.hh.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- /home/Jenkins/jenkins/F123-windows32-release/flow123d/src/coupling/time_governor.hh
- /home/Jenkins/jenkins/F123-windows32-release/flow123d/src/coupling/time_governor.cc
 1.8.7
1.8.7